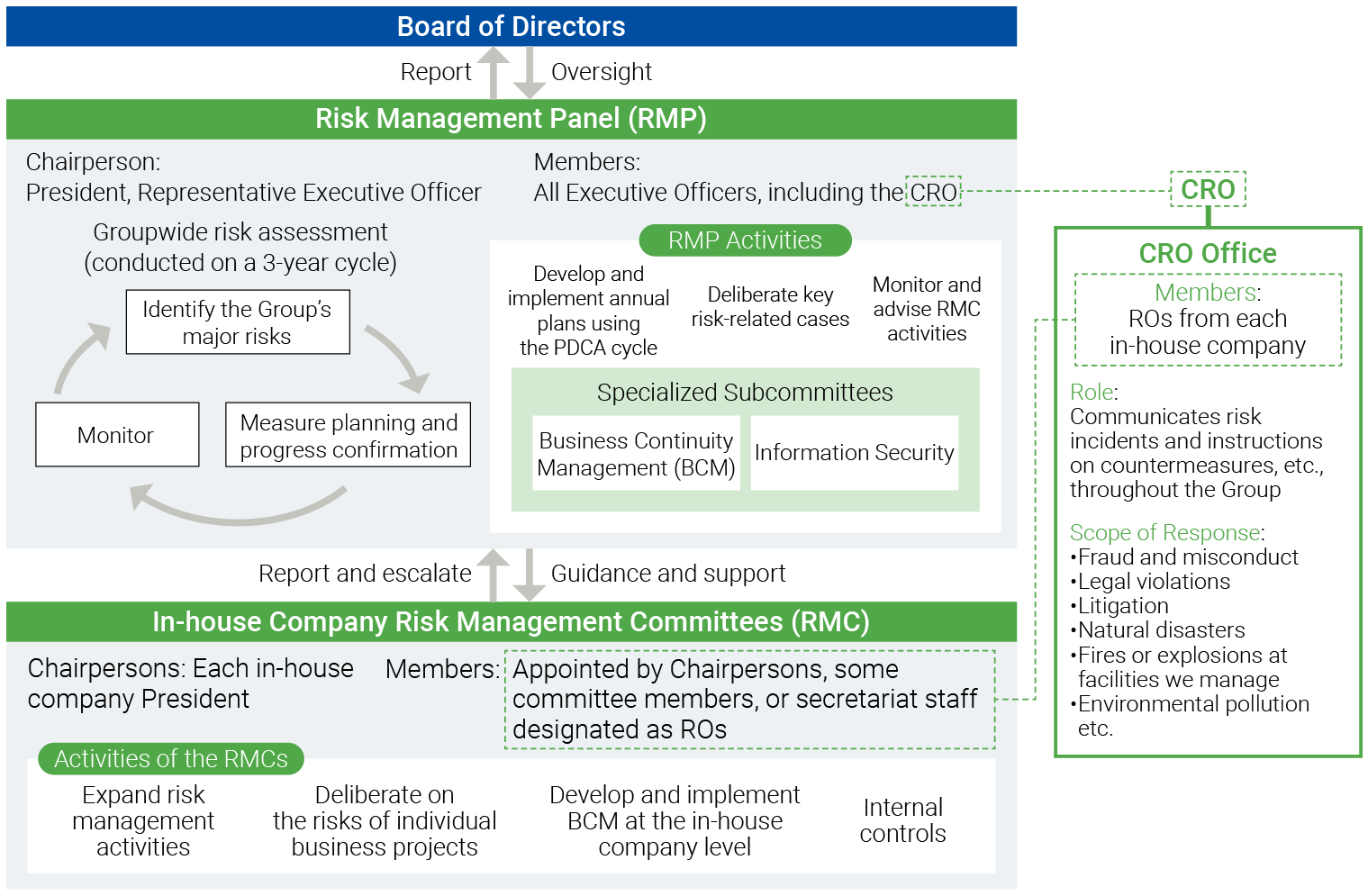
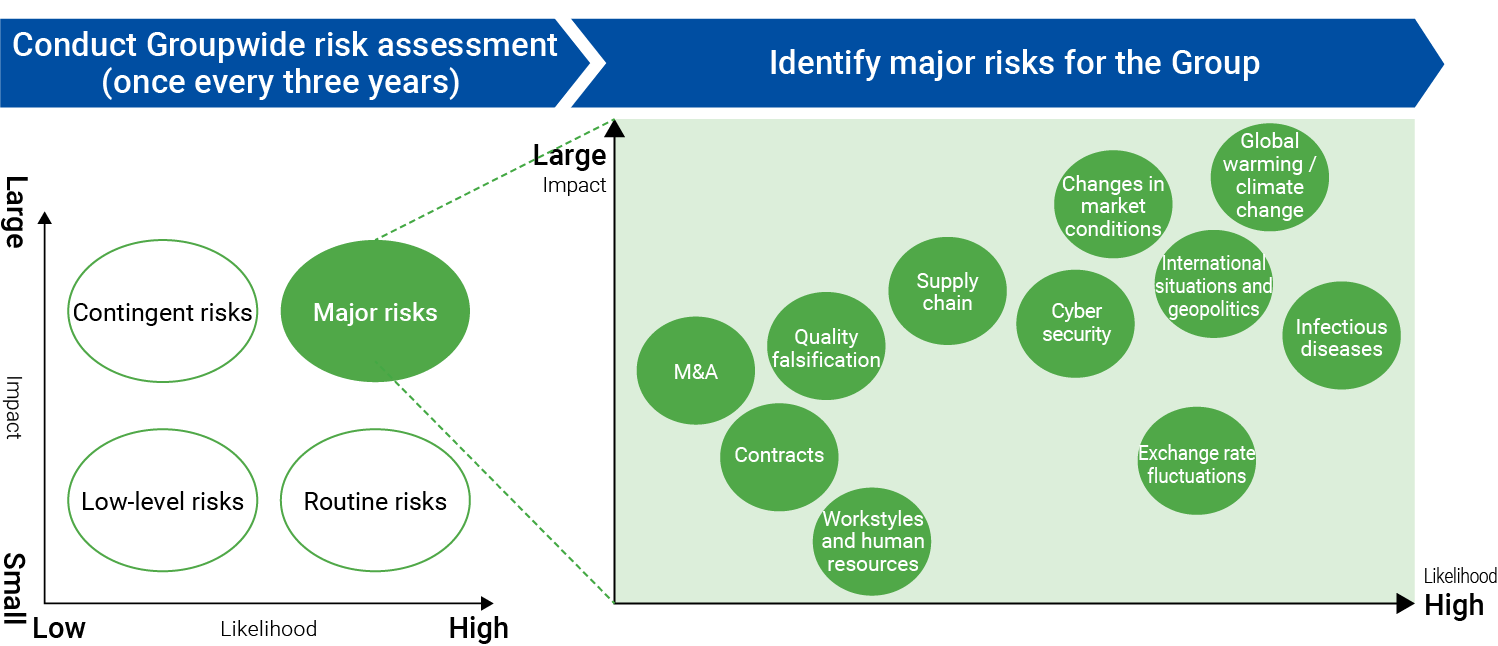
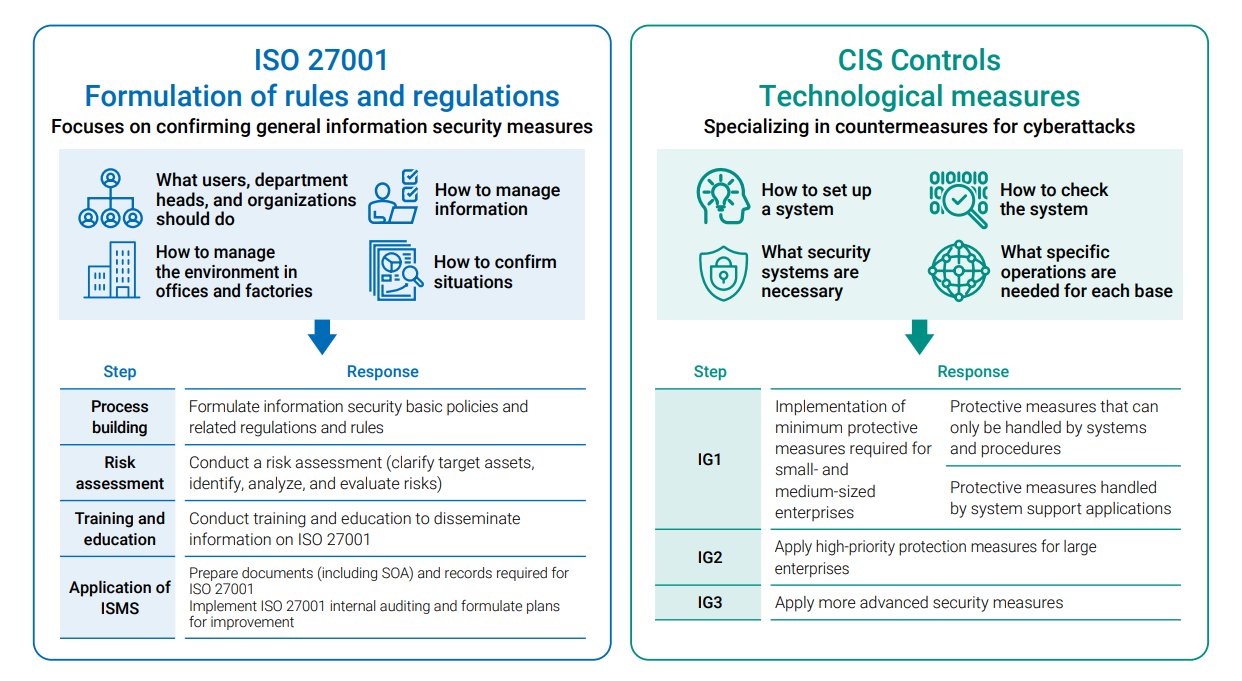
| No. |
Item |
Impact and Likelihood of Occurrence |
Risks |
Countermeasures |
| 1 |
Global environment and climate change |
High impact and high likelihood of occurrence |
- The move toward decarbonization could increase the burden of costs such as carbon taxes, and could also lead to major changes in industrial structure, such as the substitution of fossil fuels
- Intensification of typhoons, volcanic eruptions, and other natural disasters
|
- BCM plan development and continuous improvement based on hazard information, etc.
- Development of guidelines for volcanic eruptions
|
| 2 |
International situation and geopolitical risks |
High impact and high likelihood of occurrence |
- Unexpected restrictions and expenses in business activities due to impacts on economic, financial, and trade conditions stemming from political factors such as the intensification of trade friction between the United States and China, conflict in the Middle East, the situation in Ukraine, and the situation in East Asia
|
- For individual incidents, a task force headed by the President and composed of related Executive Officers will be established, depending on the situation
- As an overall response, develop global supply chains and value chains in light of risks
- Analysis of risk scenarios and development of action plans to prepare for emergencies
|
| 3 |
Changes in market conditions |
High impact and high likelihood of occurrence |
- Risk of not being able to respond to economic fluctuations and changes in market conditions
- Risk of misreading changing customers' needs
- Risk of failing to catch up with technological innovation and becoming obsolete
- Risk of dependence on specific customers or markets
|
- Each Executive Officer is responsible for identifying and managing risks related to management business strategies based on the segregation of duties, and important matters are deliberated by the Management Meeting
|
| 4 |
Risk of infectious disease |
High impact and high likelihood of occurrence |
- In addition to human life and health, lockdowns faced in response to the spread of COVID-19 and the supply chain disruptions triggered by it, as well as changes in working styles and information security issues, could have a tremendous impact on new infections that may occur in the future
|
- Strengthening BCM plans for infectious diseases
- Collaboration with industrial physicians to prevent infection and its spread
- Strengthening supply chain management capacity and planning to review efforts made to date, and revise our response guideline
|
| 5 |
Cybersecurity risks |
High impact and medium likelihood of occurrence |
- External cyber-attacks, human negligence by the Company or contractors, as well as natural disasters, infrastructure failures, or other unforeseen events, could result in the suspension of important operations and services, leakage of confidential and personal information, and destruction or falsification of important data
|
- Strengthening of software/hardware measures and development of ISO 27001-compliant systems
- Education and training for employees and temporary staff regarding information security
- Strengthening supply chain management capacity
- Clarifying policies to respond to generative AI
|
| 6 |
Risk of foreign exchange rate fluctuations |
High impact and small likelihood of occurrence |
- Effects of foreign exchange rate fluctuations on business performance
|
- Appropriate foreign exchange risk hedging measures, including exchange contracts
|
| 7 |
Risk of quality deception |
High impact and small likelihood of occurrence |
- Although the Group has strengthened its global quality control system, there have been scattered incidents at other manufacturers, and we are taking precautions to prevent such incidents from occurring in our Group
|
- Establishment and operation of a system that does not allow human judgment in data measurement
- Implement front-loading design reviews of customer specifications at the quotation stage
- Continuously improve the organizational culture and quality culture through hearings, etc.
|
| 8 |
Supply chain risk |
High impact and medium likelihood of occurrence |
(In addition to risks related to the supply chain due to the global situation and infectious diseases)
- Risk of ESG/SDGs issues caused by suppliers, such as repression of human rights
- Business continuity risk, such as business closures due to suppliers’ succession issues
- Response to the tightening of regulations for the protection of small and medium-sized businesses
|
- Strengthen monitoring of human rights and other ESG-related issues for suppliers
- Secure alternative suppliers
- Establish a cooperative system for supply chain BCM
- Step up human rights due diligence efforts
- Strengthen the legal compliance system
|
| 9 |
Risks related to working styles and human resources |
Medium impact and small likelihood of occurrence |
- Risks related to increasing and strengthening the human resources needed to achieve E-Vision 2030, and risks related to education and training to keep up with rapid changes in the work environment
- Impact on employees’ mental health, etc., due to the rapid change in their working styles caused by the spread of COVID-19
|
- Develop and utilize a human resources data bank, reinforce and review compensation and training systems
- Improve communication and implement mental health measures
- Enhance engagement based on global engagement survey results
|
| 10 |
Contract risks |
Medium impact and small likelihood of occurrence |
- A liability clause could result in very large losses in the event of a problem
|
- Continue to strengthen negotiation and legal check systems at the time of signing contracts
|
| 11 |
M&A risks |
Medium impact and small likelihood of occurrence |
- Failure to achieve business investment results
- Although M&As are an effective means of expanding into the global market, the Group does not have significant experience in M&As
|
- Implement thorough due diligence and strengthen cooperation with external advisors
- Increase the number of people with M&A experience and transfer their experience, including tacit knowledge
- Strengthen the PMI system to promptly incorporate M&A into the Group’s management
- Build up and utilize expertise in PMI implementation
|